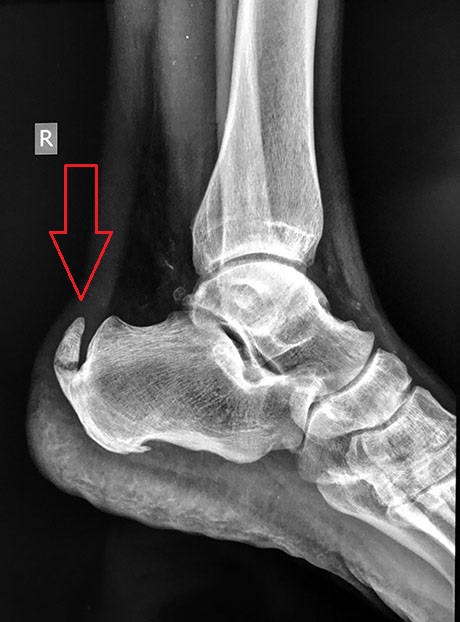
HAGLUND'S DEFORMITY
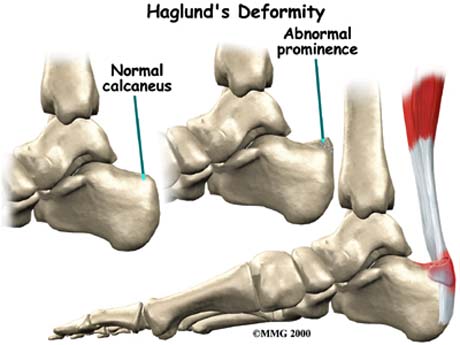
Haglund syndrome involves painful swelling of the soft tissues of the posterior heel just anterior and superior to the Achilles tendon insertion, associated with lateral calcaneal bursitis and Achilles tendinitis.
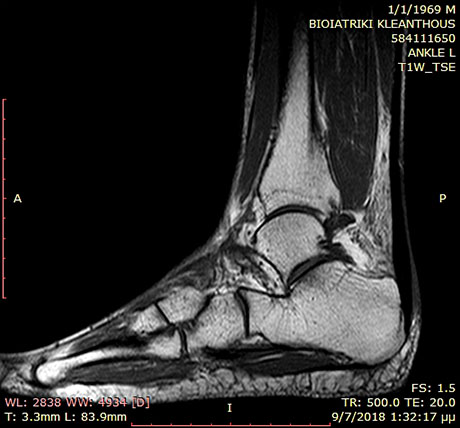
Normal hintfoot without deformities (MRI procedure)
Haglund deformity creates pain for the patient due to locally generated inflamation and Achilles tendon injury
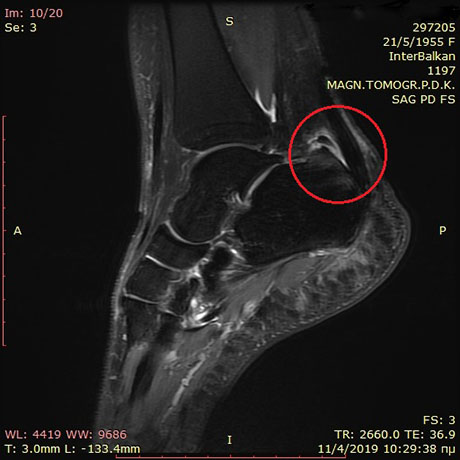
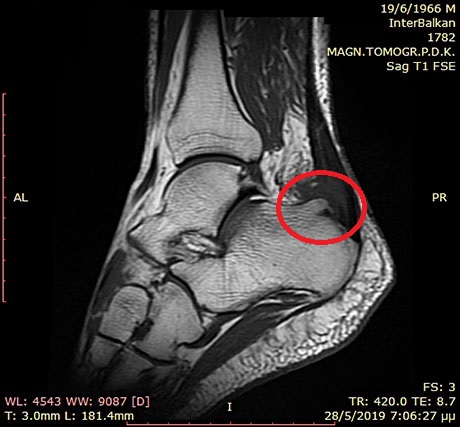
MRI ankle and foot. Osteophyte in the posterior heel which injures the Achilles tendon causing pain to the patient especially when walking
Posterior heel edema due to retrocalcaneal bursitis and Haglund deformity
CAUSES
To some extent, heredity plays a role in Haglund’s deformity. People can inherit a type of foot structure that makes them prone to developing this condition.
For example, high arches can contribute to Haglund’s deformity. The Achilles tendon attaches to the back of the heel bone, and in a person with high arches, the heel bone is tilted backward into the Achilles tendon. This causes the uppermost portion of the back of the heel bone to rub against the tendon. Eventually, due to this constant irritation, a bony protrusion develops and the bursa becomes inflamed. It is the inflamed bursa that produces the redness and swelling associated with Haglund’s deformity.
A tight Achilles tendon can also play a role in Haglund’s deformity, causing pain by compressing the tender and inflamed bursa. In contrast, a tendon that is more flexible results in less pressure against the painful bursa.
SYMPTOMS
Haglund’s deformity can occur in one or both feet. The signs and symptoms include:
- A noticeable bump on the back of heel.
- Pain in the area where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel.
- Swelling in the back of the heel.
- Redness near the inflamed tissue.
EXAMINATIONS
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
Noticeable change of normal anatomy back heel with edema - swelling and redness.
Palpation:
Patient present with deep posterior heel pain, fullness and tenderness with palpation medial and lateral to the Achilles tendon, and increased pain during dorsiflexion.
X-RAYS
Lateral foot radiographs will demonstrate Haglund deformity.
MRI and ultrasonography can be helpful to determine extent of Achilles tendon degeneration.